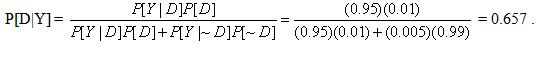A blood test indicates the presence of a particular disease 95% of the time when the disease is actually present. The same test indicates the presence of the disease 0.5% of the time when the disease is not present. One percent of the population actually has the disease. Calculate the probability that a person has the disease given that the test indicates the presence of the disease.
- 0.324
- 0.657 Correct Answer
- 0.945
- 0.950
- 0.995
Solution: B
Let
Y = positive test result
D = disease is present (and ~D = not D)
Using Baye’s theorem: